What is Protected Health Information (PHI) and HIPAA?
Last Updated on September 16, 2023
Every time we go to the hospital for a medical checkup, book an appointment with a specialist, pay medical bills, etc., it all goes into our medical records. These activities are all private data that should be protected. In a world where data is the new gold, we need to understand how personal health data is protected.
In this article, we will highlight the importance of data privacy and organizations that protect health information. Also, we will talk about what type of information is considered protected health information, how to avoid privacy violations, and the different ways we store PHI nowadays.

Definitions Related Protected Health Information (Phi)-Hipaa
According to the HIPAA rule, Protected Health Information (PHI) is simply the identifiable health information of an individual. Identifiable health information of an individual is the Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on a person’s medical record obtained while interacting with a covered entity.
There is also Electronic Protected Health Information (EPHI) which is PHI stored, sent, and created in electronic form. HIPAA is a US law to protect protected health information. As we go forward, you will learn more about PHI HIPAA and how HIPAA helps avoid data breaches in the health sector.
What is HIPAA Law? (Health Insurance Portability And Accountability Act)
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, and it is federal legislation created by the government to protect the sensitive medical records of people. HIPAA law protects patients’ information from being disclosed even without their consent. HIPAA Privacy law was passed in 1996, with the HIPAA primary purpose of creating national standards that will help prevent privacy or data breach.
Medical records, billing plans, and other protected health information are required by doctors, coding/billing companies, healthcare professionals, healthcare organizations, health insurance companies, etc. HIPAA Privacy law provides a privacy standard to protect patients’ data. To implement the requirements of HIPAA, the HIPAA Privacy Rule was issued by The US Department of Health and Services.

The Privacy Rule of HIPAA
There are individuals, organizations, and agencies known as ‘covered entities, and they are anyone in health care that provides treatment, payment, and operations. The Privacy Rule was issued to regulate the use and disclosure of personal health information by a covered entity. The goal of the HIPAA medical privacy rule is to ensure that health information is protected and allow the free flow of health information needed by covered entities to improve healthcare.
How to Become HIPAA-Compliant?
Being HIPAA compliant is important if you want to work with data or do business in the healthcare sector. Also, being HIPAA compliant means, you understand the following;
- -What HIPAA stands for
- -Strictly adhere to the Personal health information Act
- -You can prove to healthcare organizations that you have Implemented necessary measures to ensure the privacy of personal health information,
- -Maintain the integrity, provision, and confidentiality of any protected health information given access.
The US Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights has condensed the full text of HIPAA (45 CFR Parts 160, 162, and 164) into 115 pages for businesses to apply if they want to become HIPAA compliant. There are penalties for HIPAA violations or breaches of patient privacy.
The HIPAA Compliance Checklist is a good starting point for a business that wants to provide services in the healthcare industry. The checklist helps businesses access the policies and safety measures to become HIPAA compliant. Some third-party HIPPA solution providers know all about HIPAA and help businesses confirm that their policies and methods do not violate HIPAA rules.
To become HIPAA compliant, there are 4 rules that must be adhered to. These rules include;-HIPAA Privacy Rule-HIPAA Security Rule-HIPAA Enforcement Rule-HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
HIPAA Privacy Rule
The HIPAA privacy rules are laid down by federal guidelines created by the government to protect the privacy of health information. The HIPAA privacy rule regulates how protected covered entities access health information. Healthcare privacy rules are essential to prevent the misuse of data by phi healthcare providers. For example, billing information is protected under HIPAA.
HIPAA Security Rule
The Security Rule is a subset of the Privacy Rule and applies to Protected health information. HIPAA security rule protects protected health information from external threats. The Security Rule charges covered entities to implement technical, physical, and administrative safety measures to safeguard protected health information. For example, physical safety measures require storing protected health information in a safe environment.
HIPAA Enforcement Rule
HIPAA Enforcement Rule spells out investigations, procedures, and penalties for violating HIPAA rules.
HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
The final rule that must be followed is the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule which requires that when there is a breach affecting more than 50 people, covered entities should report it to the Human Health Services (HHS).
The HIPAA Journal will help you learn more about how to become HIPAA Compliant.
What is The Meaning Of PHI?
PHI meaning in healthcare refers to personal information like Demographic location, physical and mental history, blood work and test results, insurance plan, and other relevant information of an individual that is obtained by a medical professional to identify that individual and to administer care.
What is The Protected Health Information Under HIPAA?
Under the HIPAA Protected Health Information definition, goes beyond the personally identifiable information of an individual. HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, and it is a federal law by the US government that ensures the use, transit, and disclosure of PHI data. The definition of PHI under HIPAA states that phi is personally identifiable information (PII) that can be used to describe a person’s medical condition at any point in time.
Protected health information under HIPAA refers to the person’s medical records, name, and location. PHI and PII meaning relate to one another, and their examples are similar. Examples of PHI under HIPAA are names, email addresses, SSN, etc. Also, all PHI data that can be used to identify a person’s medical record is known as an identifier. HIPAA Protected Health Information identifiers cannot be regarded as PHI if they link to an individual’s medical record.
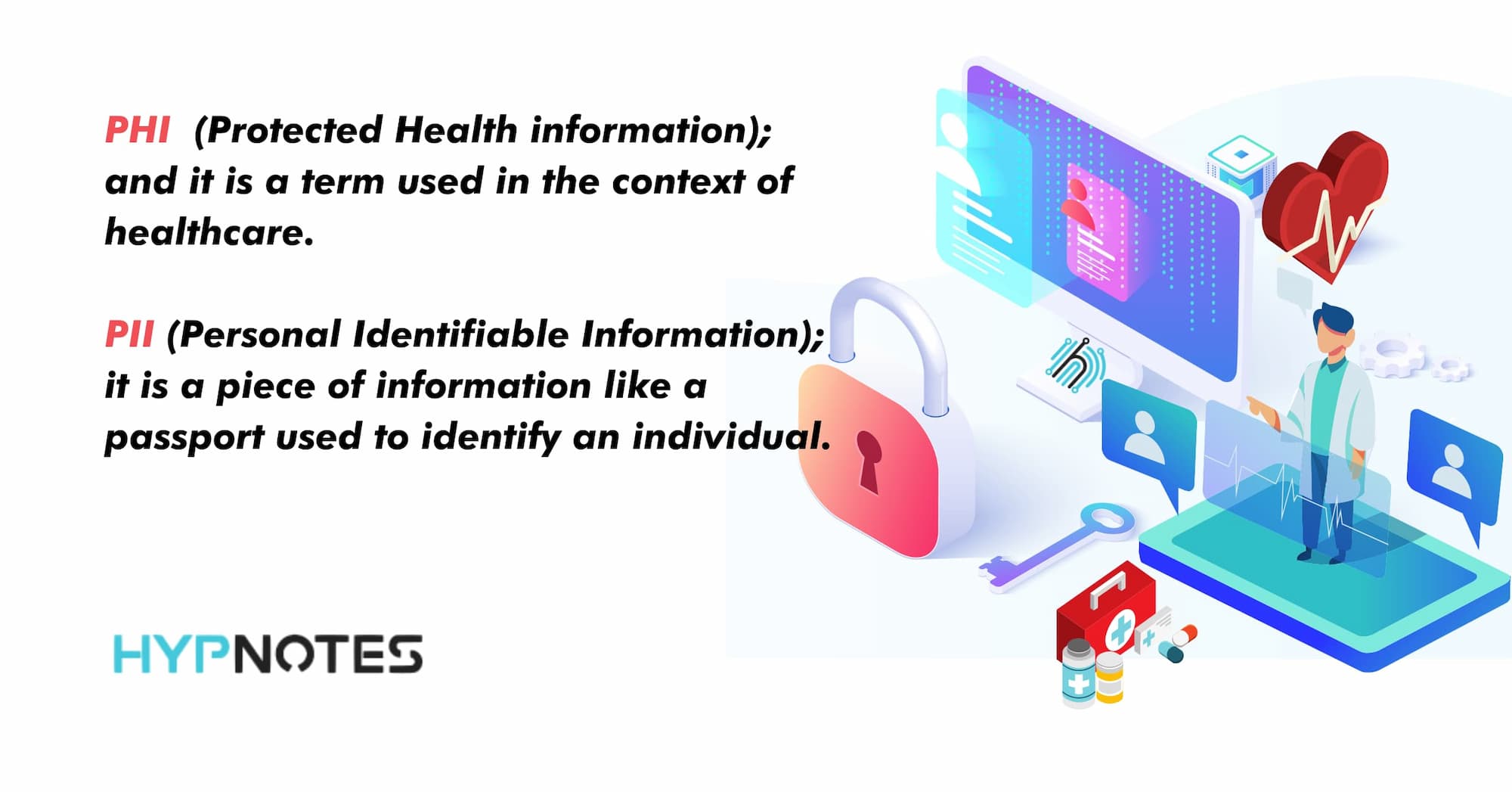
Are PHI, PII, and IIHA the Same?
No, they are not all the same. PHI stands for Protected Health Information, and it is a term used in the context of healthcare. PII stands for Personal Identifiable Information. It is a piece of information like a passport used to identify an individual. PII is not a term used in the context of healthcare, and it may not be considered PHI. IIHA stands for Individually Identifiable Health, and it is similar to PHI. Therefore, PHI and PII information is not the same, but PHI and IIHA mean the same.
What is ePHI Electronic Protected Health Information?
Electronic Protected Health Information has simply Protected Health Information (PHI) in electronic form. ePHI is defined as data that is produced, saved, and transmitted electronically. HIPAA electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) is covered under the HIPAA rule of 1996, and there are penalties for violation
Individuals, Organizations that work with ePHI data are also referred to as covered entities. HIPAA Security rule guidelines must be followed when handling ePHI. The integrity, confidentiality, availability, and ePHI security are handled by covered entities, and they must do this following HIPAA security.
What is Considered ePHI or PHI?
Looking at both abbreviations, it is easier to assume what type of information to consider as PHI and ePHI but it is not as straightforward as it looks. In order to create a HIPAA compliance program, It is important for organizations to know what ePHI /PHI is about and where it resides.
To define PHI in healthcare means Individually Identifiable personal information, a subset of health information that can be used to identify an individual. It includes;- Demographic information collected from an individual.- The information relates to the physical and mental condition of an individual presently, in the past, and in the future- An individual’s provision of health care and payment for health care can be used to identify an individual.
Depending on the context in which a piece of information is being sent, the means of communicating used may be considered a PHI or not. For example, A company sends out emails to employees with a health condition. The email is considered a PHI because it can be used to identify employees with that health condition. In another example, when a healthcare provider sends an email to a business associate that does not contain any protected health information that can be tied to anyone, that email cannot be considered a PHI.
Looking at ePHI, ePHI definition is straightforward. protected health information includes; PHI transmitted by electronic media or maintained in electronic media; hence the name electronic PHI.
The Privacy Rule contains a list of 18 identifiers for data de-identification; according to some, these identifiers are considered to be PHI. The main focus should be the context in which the identifiers are being used, especially if there is a reasonable reason to believe an individual can be identified using the information.
When considering what PHI or ePHI is, it is not enough to look at just PHI meaning, electronic protected health definition, ePHI meaning, or what ePHI information is about. One important aspect to always look out for is the context in which the information is being used. Without a clear understanding of what data is considered PHI/ePHIi, covered entities are at risk of violating the HIPAA rule
Protected Health Information Identifiers – List of 18 PHI Identifiers
An identifier is a piece of information that can be used to identify an individual, and if the identifier is used in conjunction with an individual’s health condition, then the identifier becomes protected health information. There are 18 protected health information identifiers as listed by HIPAA.
- Name
- The address includes street address, including street address, city, county, and zip code.
- All elements (except years) of dates related to an individual (including birthdate, admission date, discharge date, date of death, and exact age if over 89)
- Telephone numbers
- Fax number
- Email address
- Social Security Number
- Health plan beneficiary number
- Account number
- Certificate or license number
- Vehicle identifiers and serial numbers, including license plate numbers
- Device identifiers and serial numbers.
- Web URL
- Internet Protocol (IP) Address
- Finger or voice print
- Any other characteristics that could uniquely identify the individual
Examples of PHI
Any information in a medical record that can be used to identify an individual has protected health information. Also, when providing health care, any information created, disclosed, or used by a covered entity or business associate is another example of protected health information. PHI examples include all the identifiers listed above. Other types of PHI examples include different forms of communication or documents that can identify the health or mental condition of someone at any point in time. They include;
- Doctors or Hospital Billing information
- An email from your doctor’s office about a medication or prescription you need
- Appointment scheduling note with your doctor’s office
- MRI scan- Blood test results- Phone records
Examples of Things Not Considered to Be PHI
As you would have imagined, does it mean when a covered entity like a doctor calls out the name of a patient, then the doctor just violated a privacy rule? The answer is No because not all personally identifiable information (PII) is protected health information (PHI). As long as the information does not link to an individual’s health record, it cannot be protected health information.
For example, employment records of a hospital are not considered PHI because it does not link to an employee’s medical records even if the employment records contain personally identifiable information about the employee.
What is a Covered Entity Under HIPAA?
The objective of HIPAA is to protect the privacy of personal health information; all covered entities must comply with the rules of HIPAA and maintain the privacy of protected health information. Business associates and covered entities are also under the rule of HIPAA.
When a covered entity engages a business associate to help carry out its duties, there should be a clear arrangement and documentation of what the business associate will be handling, and all activities must be in line with the HIPAA rule. As mentioned earlier, there are features under the HIPAA that will make an organization, individual, or agency considered a covered entity.
Covered Entity Examples
As mentioned earlier, covered entities can be organizations, individuals, or agencies that work with health information and are subject to the Privacy Rule. Examples of Covered Entities are;
Hospital Care Providers
Hospital workers work with protected health information to improve health and provide health care. These include providers such as:
- Doctors
- Clinics
- Therapists
- Psychologists
- Hypnotherapists
- Dentists
- Chiropractors
- Nursing Homes
- Pharmacies
Health Plan
This includes:
- Health insurance companies
- Health Maintenance Organizations
- Company health plans
- Government programs health care plans, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and other plans for military personnel and veterans of war.
Healthcare Clearinghouse
Healthcare clearinghouses are entities that check medical claims by healthcare providers and ensure payment is processed by the insurance. They act as the middleman between healthcare providers and insurance. They are HIPAA compliant and must not transfer personal health information to payers, providers, and other business associates.
What is Permitted to Use and Disclose?
Healthcare is essentially fueled by information. Also, healthcare providers like doctors and medical personnel use the information to provide healthcare, improve the quality of healthcare, etc. Other covered entities also need the information to process billing plans and quotations. The quicker it is to access information, the faster and better healthcare provision will be.
There has been confusion by covered entities on when to share protected health information. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT (ONC), and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has proffered to solve the confusion by creating fact sheets on when to share identifiable health information.
One fact sheet is that protected health information can be shared between covered entities as long as it falls under the HIPAA definition of ‘health care operations’. Another fact sheet when protected health information can be shared is that it must be for healthcare provision or treatment. Nevertheless, sharing information must comply with the HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules.
How should Protected Health Information be Stored?
Medical records are private information that requires security from unauthorized personnel. Also, the method of storing is important because HIPAA law for storage of personal health information states guidelines, limitations, and requirements to avoid violation.

Physical Storage
For a while, physical storage has always been the most common means of storing protected health information. Storing paper records in cabinets, shelves, etc., are a popular method used in physical stores. Sending out information should be done following HIPAA law for storage and disposal of health.
Electronic Storage
With the advancement in technology, we know that PHI can be stored and transmitted electronically. Healthcare providers can easily store large amounts of data using services like Cloud computing while obeying HIPPA cloud storage rules. For example, Practice Management Software (PMS) & EHRs have been implemented by over 90% of healthcare providers in Australia. EHR stands for electronic health record, depending on the data stored, and its architecture can either be public, private, hotel, or hybrid.
Wearable Technology
Within the last decade, there has been a rise in the use of wearable technology like smartwatches, blood pressure monitors, ECG monitors, and biosensors. These devices can be used to store protected health information.
Companies producing wearable technology track the health and fitness capacity of users. There has been concern about the privacy of users because the companies producing these devices are not covered entities, so they are not HIPAA compliant.
Mobile Apps
Mobile applications have made healthcare provision easier and essential for many people, especially old patients. Patient behavior, perceived behavioral intentions, etc., led to the adoption of mobile healthcare applications. These apps are used to store and transmit PHI and need to be HIPAA compliant to avoid violation. Users can check application reviews to determine the legitimacy of these applications.
Conclusion
Protection of medical records is necessary as Health Information is private data and should be treated as such. The HIPAA rule was created to avoid privacy breaches and set guidelines to ensure the smooth distribution of health data because information dissemination is also necessary for the development of Healthcare.
Furthermore, there has been confusion regarding what type of data should be considered protected health information. The HIPAA rule makes us understand that as long as the information can lead to the identification of a person’s medical history at any time, then the information is considered a PHI. From the article, we can tell what protected health information (PHI) is and also understand that there are consequences for violating the rules in place for protection.
How Hypnotes provides Protected Health Information and HIPPA

Hypnotes practice management software takes confidentiality and data security very seriously. In fact, we consider it one of our top priorities. All of the data that is housed in Hypnotes is fully encrypted and secured by a farewell. We ensure our clients and your clients have the highest level of security regarding your data. Hypnotes is a HIPAA compliant software and provides HIPAA compliant video conferencing.
Our platform servers are housed in a protected facility 24/7 365 days a year. Our security team regularly tests our systems to ensure your data is safe from any threats. Each and every client has to go through both email and phone verification for authentication. Only verified clients can access the data that is in their accounts. We do not reveal any data to third-party companies including insurance companies.

